We are what we repeatedly do. Excellence, then, is not an act, but a habit. — Will Durant
Businesses are a constantly evolving system. How to enable excellence in a business system? This is the basic question but the important question is how to make excellence sustainable. Is it something that we can continuously assess and address? Or is it an abstract idea and elusive thought we need to ponder.
Excellence means being outstanding or extremely good at things we are doing. It is what every management would aspire their organization to be. But, just having an aspiration won’t take them there. The organization needs to work hard and strive harder for it, and then with practice and more practice it can come closer to that state of excellence.
Model is something that every organization would try to emulate, if it has been proven successful and are giving desired results. To design and develop any product, solution or framework we need to start with a conceptual understanding as a model. The concrete idea comes from abstract thought.
When we combine all three keywords Business, Excellence & Model in a meaningful manner, we arrive at the term Business Excellence Model (BEM).
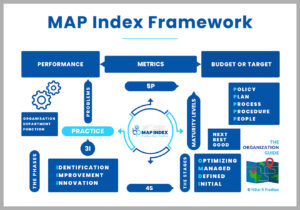
There are certain salient characteristics to the formation of framework. The framework attempts to holistically look at the organization. The framework attempts to provide a means for self-assessment. The framework assesses the various strengths and weakness of the organization. The objective is to work on those weakness and leverage on those strength to significantly improve the overall organization performance. To perform and produce results is the ultimate aim of every organization’s management – how to keep producing better business results. No framework can work without building the foundation. Hence, the pertinent questions need to be asked;
- What is the base of BEM on which organization stands?
- What are the principles on which the BEM works?
- What are values and concepts on which BEM is driven?
Not just one, there are multiple such business excellence models developed and popularized. Some of the most popular ones are; US’s Malcolm Baldrige, Europe’s EFQM Excellence Model, Singapore’s Quality Award Framework to Canadian Framework for Excellence to Australian Business Excellence Framework. Most of these countries have introduced their model of BEMs as a form of national award program for promoting and rewarding work of excellence in organizations. At the core of all such business excellence models are designed to guide management and facilitate to improve organization-wide performance. Largely, BEMs encompasses every aspects of the organization management.
The basis of Business Excellence Model (BEM) have emerged and evolved from the earlier working of quality management in organizations under the broader canvas of Total Quality Management (TQM). The quality management started with principles of quality inspection, control and then management. It is the culmination of all these streams leading to the bigger and broader movement of Total Quality Management (TQM). This quality movement has been building over the last 75 years and picking in the mid 80s. The bulk of the quality movement activities started in Japan and then rapidly progressed to US. These ideas were championed by quality gurus like Deming, Juran and Crosby, conceptually revolving around the Toyota Production System (TPS).
Change is inevitable and change in TQM was long waiting to happen – these three words were replaced with BEM with many more things and much more reinforcement to the framework to make it concrete and comprehensive. Hence, BEM has been the natural extension to TQM which also was comprehensive by being total in nature. However, BEMs are much more than TQM which is primarily designed to build a broad quality management system in the organization.
BEMs are fundamentally designed to serve two purposes. Primary purpose is to guide organization towards achieving excellence and secondary purpose is to conduct assessment. The core values and concepts are at the centre of BEMs. Unless the value system and conceptual models are embedded into core of the organization, no management framework can work. Malcolm Baldrige, EFQM and Deming Prize are three most popular models in the market. These models encompass much bigger spectrum making an all-encompassing coverage of the organization management. This framework includes the following set of criteria’s which in turn comprise of practices.
- Visionary Leadership
- Policy Formulation
- Strategy Framework
- People Management
- Partnership Management
- Resources Management
- Knowledge Management
- Innovation Management
- Organizational Learning
- Customer Experience
- Customer Results
- Employee Results
- Society Results
- Business Results
Each of the aforementioned criteria has a set of practices but the big question mark remains in the usability of such practices. Though these BEMs have been in use across large companies and in different countries there remain common difficulties. The difficulties are in the form of complicated set of assessment criteria, and the tedious procedures to too much paperwork. The degree varies with context and there are software tools to assist the implementation but the ease of usability is of concern to mangers.
There are two sides to the various research findings on BEMs. Some research indicates that its implementation results in better business results and there are other reports suggest it doesn’t guarantee business success. These inferences drawn could be attributed to many things; some are visible and others are invisible in nature like the management’s level of commitment to such comprehensive organization change, people’s degree of involvement, employee’s motivation level, fear of change, resistance to learn new skill, always resource limitations for such big change program to making fundamental changes to organizational structure and culture.
Organization uses these BEMs for continuous performance improvement much like the TQMs. Is it used in a particular way or there are different ways to use the models. There are no standard rules, hence organizations can use in different ways. They can use it for assessment purpose or they can design a performance management system out of it or they can use it as means to benchmark with similar organizations in the industry.
Essentially speaking, BEMs as frameworks are widely employed by organizations to appraise themselves, the internal health-check and then advance the working of management practices. Thereby building on business performances to grow and gain. However, there are couples of challenges to the process of implementation and to the manner of usage of these models.
- First point is to respond to so many question statements under different criteria, not easy for managers to do so objectively.
- Second point is that; none of the models provide solutions to the problems faced by the organization.
BEMs are conceptually strong in their presentation to provide an overall guidance to the workings of management but find operationally weak when put to practice in the organization. In a way, we can infer that inspite of its holistic perspective the practicality part remains to be worked upon. BEMs are models and as discussed these models have their inherent limitations and the challenges manager face during implementation are there to be seen.
Hence, BEM was been transformed into BEF i.e. Business Excellence Framework as was the case from TQM to BEM. There are two very important setups needed to be rest for a successful implementation of BEM; one is that of setting the right culture in the organization and having the right set of management tools & techniques.
For example, at the planning level techniques used such as SWOT to Segmentation Targeting Positioning (STP) and at operational level tools used such as Total Productive Maintenance (TPM) to Just-In-Time (JIT). Management systems need various tools and techniques to keep improving while constantly building efficiencies into the business processes. The process capabilities matter and the management bandwidth can make or break the framework.
BEF attempts to integrate these two important aspects into BEM, thereby making the model to work like a framework. Models are conceptual in nature whereas Frameworks are designed to work, hence defined as frame that works.